The Organization tab is used to define network and service architecture to ClearIP. Defining the network organization is useful for organizing or routing calls, setting up fraud control, and creating analytics. SBC devices and network structure are defined in the Organization section for ClearIP.
This feature allows for the organization of calls into various logical groupings, perhaps based on location, user attributes or different customer segments.
Network Organization
The following figure shows examples of two possible network organizations within ClearIP:
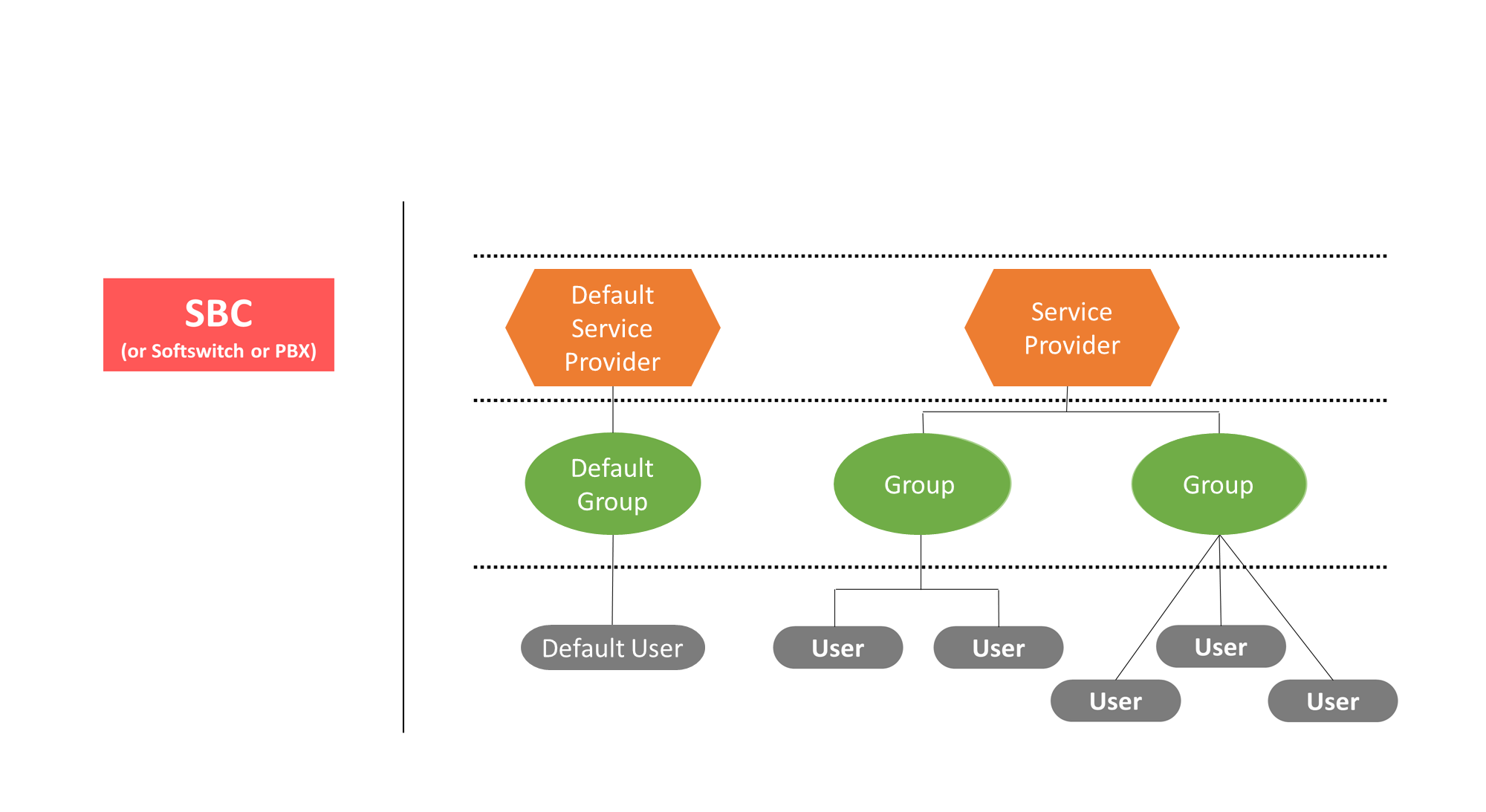
In ClearIP, all network structures can be defined as a hierarchy with up to four levels:
- Operator - a collection of SBCs, Service Providers, and ClearIP policies. Operators are considered isolated tenants within ClearIP. Each Operator can have its own set of SBCs, Service Providers, Groups, and Users, Number Translation Rules, and policies. Policies configured in one Operator do not affect calls associated with a different Operator.
- For STIR/SHAKEN authentication, each Operator must have its own STI Certificate created. If you have 2 Operators which both require STIR/SHAKEN authentication, then the STI Certificate monthly costs are double a single STI Certificate cost.
- Service Provider - a collection of Groups. A Service Provider in ClearIP is not necessarily a real service provider. Like a Group, the Service Provider is not strictly defined. To organize Groups by geography, Service Providers could be states, regions, enterprises, or something else. A Group can only belong to one Service Provider.
- Group - a collection of Users. A Group is not strictly defined. Reasonable choices for Groups typically depend on your network organization. For example, to organize Users by geography, Groups can be cities, states, or regions. A User can only belong to one Group.
- User - a call source such as a subscriber, trunk group or SIP peer. Users can be defined by only one of the following identifiers transmitted to ClearIP in a SIP INVITE message:
- IP address
- Originating trunk group
- User ID
- Calling telephone number.
The SBC (Session Border Controller) is any network device that sends SIP INVITEs to ClearIP. ClearIP uses the general term SBC to represent any SIP device, such as a softswitch, Private Branch eXchange (PBX) or SIP proxy. ClearIP only accepts SIP INVITEs from IP addresses that are configured as an SBC. All other network traffic is refused by ClearIP.
When ClearIP receives a SIP INVITE from an SBC, it matches the INVITE to a specific User, Group, Service Provider, and Operator by searching the INVITE for information that identifies the User.
In some cases, it may not be necessary to define multiple Users, Groups, Service Providers, and Operators at all, but defining them can be helpful for taking advantage of additional ClearIP features.
However, for simplicity, all calls can be associated with a single default User, Group, Service Provider, and Operator. Having a Default User ensures that every SIP INVITE from an SBC will be processed by ClearIP. Having this configuration enables the use of all ClearIP’s essential features.
Initial Setup
Add Operator
If access has been granted to the Operator page under the Organization dropdown menu, an initial Operator must be created to conduct testing. If access is not available to the Operators page, this step can be skipped.
Under the Organization dropdown menu, go to the Operators page. Click the Add button to create a new Operator. An Operator Name is the only field in the form that needs to be added. The Name can be changed at any time, so initially set the Operator Name as the organization name and adjust later if needed.
Additional Operators can be added later, based on specific network requirements.
Add SBCs
Visit SBCs for more detailed information on setting up SBCs.
For setting up the Organization tab, the public address of the Session Border Controller (SBC), softswitch, or Private Branch eXchange (PBX) is required. This is the IP address that will send SIP INVITEs to sip.clearip.com.
Click the Organization tab and select the SBCs option to display the SBC page. Click the Add button to fill out the form for adding SBCs.
- Enter a Name for the SBC and add the public IP Address of the SBC. It is recommended that the SBC Name be a meaningful name that is easy to remember.
- Select any other appropriate options. The SBC will show up in the SBC page as a row in the table.
Add Default Service Provider, Group, User
The recommended best practice for initial setup is to add a Default Service Provider, Default Group, and Default User. These default settings will ensure that every call from the SBC will be mapped to ClearIP and processed. If a call cannot be mapped to a ClearIP User, ClearIP will return a SIP 403 Forbidden message. More Service Providers, Groups, or Users can be added later, based on network requirements.
If multiple Operators have been provisioned, each Operator must be configured with its own Default Service Provider, Default Group, and Default User.
Add Default Service Provider
Click the Organization tab and select the Service Providers option to display the Service Providers page. Click the Add button to fill out the form for adding Service Providers. Add a Default Service Provider to get started.
Add Default Group
Once a Default Service Provider is created, create a Default Group within the Default Service Provider. Select the Groups option in the Organization tab and click the Add button to add the Default Group. After creating Default Group, more targeted Groups can be created to categorize calls more specifically.
Add Default User
Select the Users option within the Organization tab and click the Add button to add the Default User. In the Service Provider and Group fields, select the Default Service Provider and Default Group already created. Enter “Default User” as the Name. For getting started with the Default User, the header and tag identifier fields can be left blank. More Users can be added later is required.
Distinguish Inbound and Outbound Calls
If ClearIP will be used to simultaneously process both inbound (PSTN-to-provider) and outbound (provider-to-PSTN) calls, ClearIP must be able to distinguish inbound and outbound call directions.
If the intention is to only send calls of the same direction to ClearIP, such as only using ClearIP to monitor outbound calls, this step can be skipped.
There are primarily 3 methods for ClearIP to distinguish call traffic direction:
- Multiple SBCs are created with unique public IP addresses for each call direction. One or more IP addresses are reserved to only send outbound calls to ClearIP, and a different set of IP addresses are reserved to only send inbound calls to ClearIP.
- Multiple SBCs are created with the same public IP address but different partition values.
- A single SBC is created. Special headers or parameters contained in the SIP INVITE are used to identify inbound or outbound calls and are defined in the ClearIP Users page.
Multiple SBCs with Unique Public IP Address
In this example, there are two different Operators to distinguish inbound and outbound traffic.
| Name | Status | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| ABC Telco Inbound | Active | Use this operator for INBOUND calls to ABC Telco |
| ABC Telco Outbound | Active | Use this operator for OUTBOUND calls from ABC Telco |
Within each Operator, an SBC is defined with a unique public IP address. The switch or SBC is configured to use one external IP address to send outbound calls to ClearIP and another external IP address to send inbound calls to ClearIP.
| Operator | Name | IP Address | Partition | Status | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABC Telco Inbound | IP of SBC for INBOUND Calls | 1.1.1.1 | Active | CNAM Header is set to P-Asserted-Identity Embedded in Contact URI | |
| ABC Telco Outbound | IP of SBC for OUTBOUND Calls | 2.2.2.2 | Active | Identity Header is set to Identity Embedded In Contact URI |
When creating policies in ClearIP, the appropriate Operator should be selected to apply a service on outbound or inbound calls.
Multiple SBCs with different partition values
In this example, there are two different Operators to distinguish inbound and outbound traffic.
| Name | Status | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| ABC Telco Inbound | Active | Use this operator for INBOUND calls to ABC Telco |
| ABC Telco Outbound | Active | Use this operator for OUTBOUND calls from ABC Telco |
Within each Operator, there is an SBC defined with a different partition value. The switch or SBC is configured to use one partition to send outbound calls to ClearIP at outbound.sip.clearip.com and another partition to send inbound calls to ClearIP at inbound.sip.clearip.com.
| Operator | Name | IP Address | Partition | Status | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABC Telco Inbound | Partition of SBC for INBOUND Calls | 1.1.1.1 | inbound | Active | |
| ABC Telco Outbound | Partition of SBC for OUTBOUND Calls | 1.1.1.1 | outbound | Active |
When creating policies in ClearIP, the appropriate Operator should be selected to apply a service on outbound or inbound calls.
Single SBC with defined headers
In this example, there is one SBC and one Operator. Two Service Providers have been created for Inbound and Outbound calls respectively.
Within each Service Provider, you can define one or more Groups. In the Default Outbound Service Provider, you can create a single Group also named Default Outbound. In the Inbound Service Provider, you should create a Group for every origination carrier you use. The Group name can be set to the name of the origination carrier.
| Service Provider | Name | Status |
|---|---|---|
| Inbound | Carrier 1 | Active |
| Inbound | Carrier 2 | Active |
| Default Outbound | Default Outbound | Active |
For inbound calls, the netsapiens is configured to automatically add an X-Otg header with the trunk description and P-Source-Device with the source IP address from the origination carrier. The X-Otg value is automatically populated based on the origination trunk description in the netsapiens connection list. Here is an example SIP INVITE which includes the X-Otg and P-Source-Device headers for an inbound call.
INVITE sip:+18554742536@sip.clearip.com:5060 SIP/2.0
Via: SIP/2.0/TCP sip.clearip.com:5060
From: <sip:+14045266060@transnexus.com:5060>
To: <sip:+18554742536@sip.clearip.com:5060>
P-Source-Device: 54.245.86.152
X-Otg: carrier1
Call-ID: 123456
CSeq: 1 INVITE
Content-Length: 0
Within each Group, one or more Users can be defined. In the Default Outbound Group, a User named Default Outbound Calls can be created. When creating this User, set the Service Provider, Group, and Name fields, and leave all other fields blank.
In the Groups for the Inbound Service Provider, Users defined by the trunks used for each origination carrier can be created. The trunks should be defined by either the trunk description or source IP address but not both. For inbound Users being defined based only on trunk description, the trunk description is entered into the Originating Trunk Group field. This value must exactly match the value passed in the X-Otg header of the SIP INVITE, including capitalization and spacing.
For inbound Users being defined based only on source IP address, the IP address is entered into the P Source Device field. This value must exactly match the value passed in the P-Source-Device header of the SIP INVITE.
When creating policies in ClearIP, the appropriate Service Provider should be selected to apply a service on outbound or inbound calls. Leaving the Group and User fields blank allows the policy to apply to all Groups and Users defined under the selected Service Provider.
Define Users
Users can be defined by only one of the following identifiers transmitted to ClearIP in a SIP INVITE message:
- User ID defined by one of the following (ordered from highest priority)
- X-User-Id header
- User-Id parameter in the X-Broadworks-Dnc
- IP address defined by one of the following (ordered from highest priority)
- P-Source-Device header
- Trunk-Context user parameter in the Contact header
- From header host
- Originating trunk group (OTG) defined by one of the following (ordered from highest priority)
- X-OTG header
- OTG URI parameter in the From header
- OTG parameter in the From header
- TGRP user parameter in the Contact header
- Bill to Number defined by
- P-Charge-Info header user
- Calling telephone number defined by one of the following (ordered from highest priority)
- Diversion header user
- P-Asserted-Identity header user
- Remote-Party-ID header user
- P-Charge-Info header user
- From header user
NOTE: Capitalization of header and parameter (e.g. “otg”) names does not matter for ClearIP, but capitalization of the values does matter. All values must be less than 256 characters long and only contain numbers, letters, spaces, “#”, “+”, “.”, “,”, “(”, “)”, or “-”.
Example: SIP INVITE with User ID
If there is a user defined in ClearIP by the User ID value of 9999, ClearIP looks at SIP INVITEs for that User ID value to group calls by the defined user. If multiple User IDs are present in the SIP INVITE, the first instance is chosen from the order below.
User ID Method 1: X-User-Id header
INVITE sip:+18554742536@sip.clearip.com:5060 SIP/2.0
Via: SIP/2.0/TCP sip.clearip.com:5060
From: <sip:+14045266060@transnexus.com:5060>
To: <sip:+18554742536@sip.clearip.com:5060>
X-User-Id: 9999
Call-ID: 123456
CSeq: 1 INVITE
Content-Length: 0
User ID Method 2: User-Id parameter in the X-Broadworks-Dnc
INVITE sip:+18554742536@sip.clearip.com:5060 SIP/2.0
Via: SIP/2.0/TCP sip.clearip.com:5060
From: <sip:+14045266060@transnexus.com:5060>
To: <sip:+18554742536@sip.clearip.com:5060>
X-Broadworks-Dnc: network-address="sip:+14045266060@transnexus.com";user-id="+14045266060@transnexus.com"
Call-ID: 123456
CSeq: 1 INVITE
Content-Length: 0
Example: SIP INVITE with IP Address
If there is a user defined in ClearIP by the IP address value of 9.9.9.9, ClearIP looks at SIP INVITEs for that IP address value to group calls by the defined user. If multiple IP addresses are present in the SIP INVITE, the first instance is chosen from the order below.
IP Address Method 1: P Source Device header
INVITE sip:+18554742536@sip.clearip.com:5060 SIP/2.0
Via: SIP/2.0/TCP sip.clearip.com:5060
From: <sip:+14045266060@transnexus.com:5060>
To: <sip:+18554742536@sip.clearip.com:5060>
P-Source-Device: 9.9.9.9
Call-ID: 123456
CSeq: 1 INVITE
Content-Length: 0
IP Address Method 2: trunk-context parameter in the Contact header
INVITE sip:+18554742536@sip.clearip.com:5060 SIP/2.0
Via: SIP/2.0/TCP sip.clearip.com:5060
From: <sip:+14045266060@transnexus.com:5060>
To: <sip:+18554742536@sip.clearip.com:5060>
Contact <sip:+14045266060;tgrp=9999;trunk-context=9.9.9.9@5.6.7.8:5060>
Call-ID: 123456
CSeq: 1 INVITE
Content-Length: 0
IP Address Method 3: From header host
INVITE sip:+18554742536@sip.clearip.com:5060 SIP/2.0
Via: SIP/2.0/TCP sip.clearip.com:5060
From: <sip:+14045266060@transnexus.com:5060>
To: <sip:+18554742536@sip.clearip.com:5060>
Call-ID: 123456
CSeq: 1 INVITE
Content-Length: 0
Example: SIP INVITE with OTG
If there is a user defined in ClearIP by the originating trunk group value of 9999, ClearIP looks at SIP INVITEs for that originating trunk group value to group calls by the defined user. If multiple OTGs are present in the SIP INVITE, the first instance is chosen from the order below.
OTG Method 1: X-Otg header
INVITE sip:+18554742536@sip.clearip.com:5060 SIP/2.0
Via: SIP/2.0/TCP sip.clearip.com:5060
From: <sip:+14045266060@transnexus.com:5060>
To: <sip:+18554742536@sip.clearip.com:5060>
X-Otg: 9999
Call-ID: 123456
CSeq: 1 INVITE
Content-Length: 0
OTG Method 2: OTG URI parameter in the From header
INVITE sip:+18554742536@sip.clearip.com:5060 SIP/2.0
Via: SIP/2.0/TCP sip.clearip.com:5060
From: <sip:+14045266060@transnexus.com:5060;otg=9999>
To: <sip:+18554742536@sip.clearip.com:5060>
Call-ID: 123456
CSeq: 1 INVITE
Content-Length: 0
OTG Method 3: OTG parameter in the From header
INVITE sip:+18554742536@sip.clearip.com:5060 SIP/2.0
Via: SIP/2.0/TCP sip.clearip.com:5060
From: <sip:+14045266060@transnexus.com:5060>;otg=9999
To: <sip:+18554742536@sip.clearip.com:5060>
Call-ID: 123456
CSeq: 1 INVITE
Content-Length: 0
OTG Method 4: TGRP parameter in the Contact header
INVITE sip:+18554742536@sip.clearip.com:5060 SIP/2.0
Via: SIP/2.0/TCP sip.clearip.com:5060
From: <sip:+14045266060@transnexus.com:5060>
To: <sip:+18554742536@sip.clearip.com:5060>
Contact <sip:+14045266060;tgrp=9999;trunk-context=9.9.9.9@5.6.7.8:5060>
Call-ID: 123456
CSeq: 1 INVITE
Content-Length: 0
Example: SIP INVITE with Bill to Number
INVITE sip:+18554742536@sip.clearip.com:5060 SIP/2.0
Via: SIP/2.0/TCP sip.clearip.com:5060
From: <sip:+14045266060@transnexus.com:5060>
To: <sip:+18554742536@sip.clearip.com:5060>
P-Charge-Info: <sip:+14045266060@transnexus.com:5060>
Call-ID: 123456
CSeq: 1 INVITE
Content-Length: 0